Activu Thought Leadership in partnership with Planar
Executive Summary
Video walls serve diverse purposes across industries, from board meetings to auditoriums and lobbies. However, control rooms, particularly those with critical missions, demand unique considerations primarily centered on stringent visual performance requirements. Given the pivotal role that control rooms play, these specifications become imperative. Over the last decade, advancements in video wall display technology, particularly in Direct View LED (DV LED), have been remarkable. High-resolution indoor DV LED technology has become the preferred choice for control rooms due to its uniquely attractive features. Here’s why:
• Flexibility. Control rooms vary in dimensions, influencing video wall size, depth, shape, viewing distance and angles. DV LED technology stands out by offering a selectable pixel density, allowing control room designers to tailor specifications precisely without overspending on unnecessary pixel density or compromising image quality.
• Truly Seamless. Composed of small, thin, flat panels, and no bezels, DV LED displays are the only large display option that enables completely seamless viewing of any information, no matter the size, configuration, or aspect ratio.
• Clear View from Any Angle. Operators in a control room may view the wall from different angles. DV LED displays ensure a direct line of sight to the illuminations source, resulting in exceptional off-axis viewing and brightness uniformity, compared to alternative technologies.
• Versatile. DV LED’s compact nature enables it to fit seamlessly into less accommodating spaces. Installation methods also vary, adding to its adaptability.
• Durability & Resilience. Engineered for continuous operation, DV LED displays prove to be resilient over time, and eliminate the need for more fragile materials, such as thin plastic and glass panels
• Low Maintenance. With no need for additional parts like lamps, fans and filters, maintenance requirements are reduced. If a smaller DV LED module is damaged, the replacement is quick and easy, and the damaged component can be moved to a less intrusive area of the screen while a replacement is sourced. Because DV LED panels are typically smaller, repairs are less intrusive to the overall screen image.
• Cost-Effective Warranty Coverage. Due to low maintenance and service costs, warranty coverage for DV LED screens is notably superior and more economical.
• Alert & Monitoring System. Modern DV LED control room displays feature monitoring capabilities across key components, detecting trends in the device’s use and performance, and issuing alerts promptly to users to prevent issues from escalating.
• Power Usage & Operating Costs. DV LED power usage correlates closely with brightness and display content, yet operating costs remain comparable to rear projection displays.
• Longevity. On average, DV LED displays boast an impressive lifespan of 22 years.
The following material contains a more in-depth examination of DV LED technology, and why it is replacing older technologies in critical spaces and operation centers.
Direct View LED (DV LED) Technology in Control Rooms
Introduction
Video wall display technology has evolved significantly in recent years and as a result, the relative prevalence of the technologies in use has shifted as well. This is true across most video wall display applications including control room applications. Control rooms do, however, have special requirements of the high-resolution video wall displays they rely on as part of successfully meeting the organization’s goals. For these control room applications, Direct View LED (LED) display technology has emerged as a strong solution for meeting their visualization requirements. This paper describes some of the key characteristics that make LED technology the predominant display technology for modern control room installations.
Evolving Video Wall Display Technology
Over the past 10 years, the leading technologies for high resolution video walls have been rear projection, tiled LCD and LED. Front Projection has been sidelined from these applications primarily because it lacks the resolution, brightness and room-fit required.
These three leading display technologies have each evolved and improved over this period, typically reducing, or compensating for inherent weaknesses and building on inherent strengths. One result of these evolutions is that the market has voted and the relative prevalence of each has shifted.
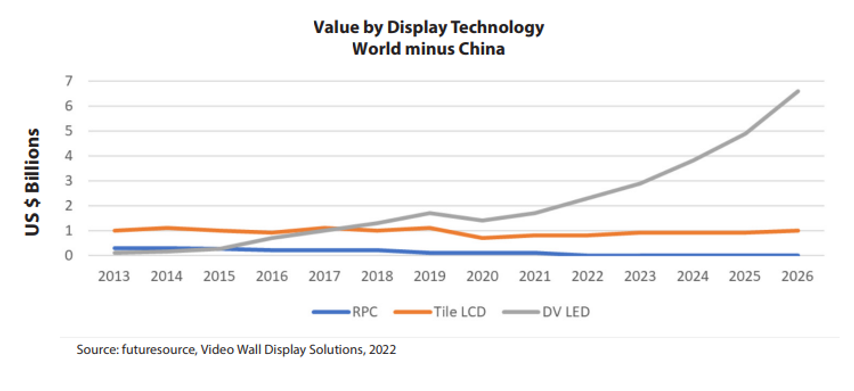
Generally, there are nine characteristics of LED technology that make it attractive for a range of high-resolution indoor applications.
Characteristics of LED
Attractive for High-Resolution Indoor Use Cases
1. Seamless
2. Great viewing angles
3. Great uniformity
4. Wide color gamut
5. Wide brightness range
6. Choice of pixel density and price points
7. Fits any physical space
8. Low cost of ownership—moudular repair
9. Long Life
There are many applications for high-resolution indoor video walls including board rooms, meeting rooms, video conference rooms, auditoriums, on-camera and in-camera backdrops, lobbies and, of course, control rooms. But control rooms have requirements and considerations beyond those of many of these other applications.
Historically, the leading display technology for many control room types has been rear projection cube technology. Therefore, in the following discussion of LED technology in control rooms, comparisons are made to the most advanced rear projection cube product specifications and characteristics.
Meeting the Specific Requirements of Control Rooms
Control rooms come in different sizes and shapes and, depending on the organization’s mission, they deliver varying types of visual content for their operators. Optimizing around the physical requirements of a control room results in video wall considerations related to wall size, display depth, shape, viewing distances and viewing angles.
Viewing Distance and Pixel Density
The viewing distance from operator to screen and the type of content being viewed will impact the optimal pixel density (pixels per square meter or square foot). Ideally you can match the pixel density to the viewing distance. More pixel density (closer viewing) than you need, and you end up paying in your processing to drive extra resolution and potentially driving content at too fine a resolution for the average viewer to see easily. Less pixel density than you need, and the visual information lacks desired clarity and sharpness.
A unique feature of LED technology is that it allows you to select pixel density from a range of choices. With LED, pixel density is typically expressed in pixel pitch, where, for instance, 1.2mm pixel pitch LED screen has 1.2mm between each pixel both horizontally and vertically. LED displays typically offer a range of pixel pitches in the same display family. A pitch range may include 0.6, 0.7, 0.9, 1.2, 1.5, 1.8, 2.0+mm and allow the control room designer to closely fit the requirements of the room and application, without overspending for unneeded pixel density or under-delivering on image quality.
One measure of viewing distance is referred to as retina distance. It is the viewing distance at which a person with 20/20 vision can no longer discern individual pixels.
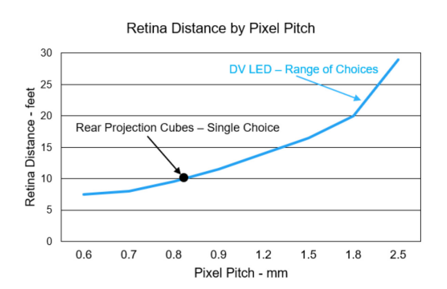
Viewing Angles
Certain control rooms require relatively wide and tall video walls. While high-use content can be positioned directly in front of an associated operator, it is not uncommon for operators to need to view visual information at an off-axis angle, whether horizontal, vertical or a combination. With sufficient room depth, video walls can be implemented in faceted concave arcs to partially compensate for restricted off-axis viewing angles created by displays with complex Fresnel and lenticular screens. For vertical viewing, front tilted walls are more problematic and much less common. As a result, video wall technology viewing angles are important.
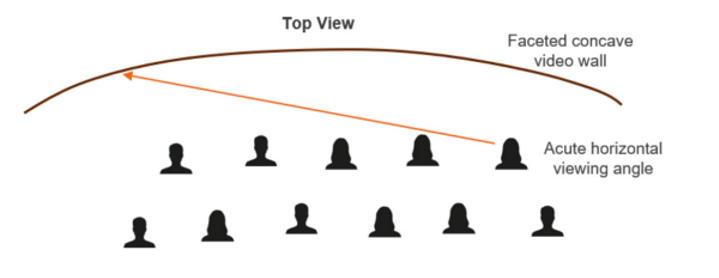
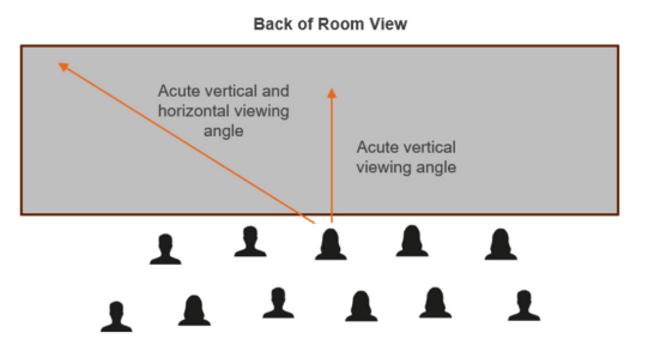
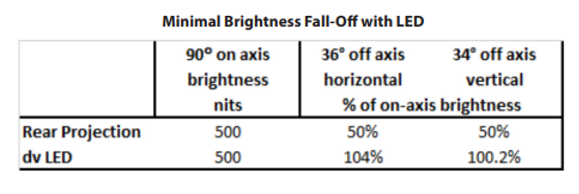
Steep horizontal or vertical viewing angles create difficult viewing when display brightness falls-off significantly as viewing angles increase. The emissive nature of LED along with modern LED package design creates a direct line of site to the illumination source resulting in outstanding off-axis viewing and brightness uniformity compared to other technologies.
The table below compares the specifications of the leading rear projection control room display to actual measurements performed on a Planar LED screen that was set to a reduced light output to match the brightness of the display cube.
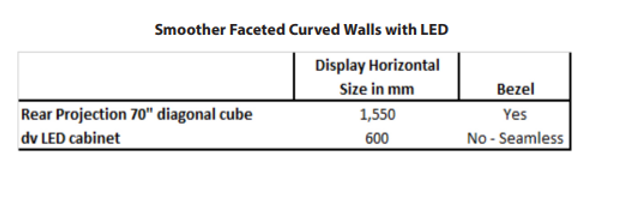
While some control rooms may use faceted concave curve designs to partially compensate for poor display technology viewing angles, others implement curved video walls for other aesthetic or operational reasons. Short of using a flexible display technology, using a smaller width display cabinet allows for smoother faceted curves where the angle of each facet can be minimized. LED technology allows for this and does it with a seamless cabinet rather than one that implements a bezel.
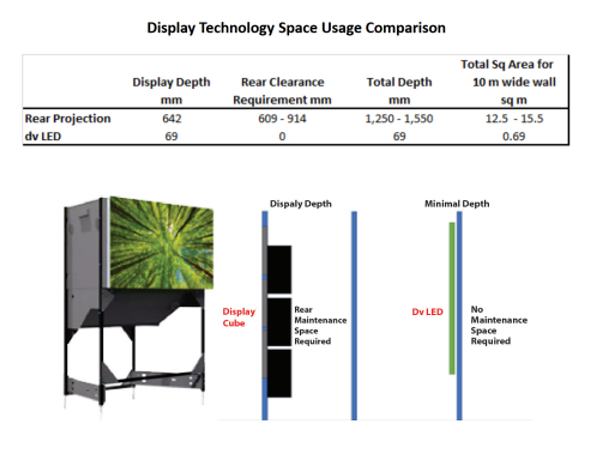
Footprint and Space Requirements
Often control rooms will have some square footage area constraints when factoring in room to accommodate the operators, the video wall or display cubes, and service space. If the video wall is significantly concave to compensate for viewing angle constraints, then that wall will take more floor space than a flat or slightly concave video wall.
Even for control rooms that have an abundance of physical space that square footage has a real cost associated with it both in terms of acquisition cost per square foot and in terms of ongoing HVAC load. It can be helpful to use a video wall technology that not only takes less room, but that can be installed and serviced using a range of methods.
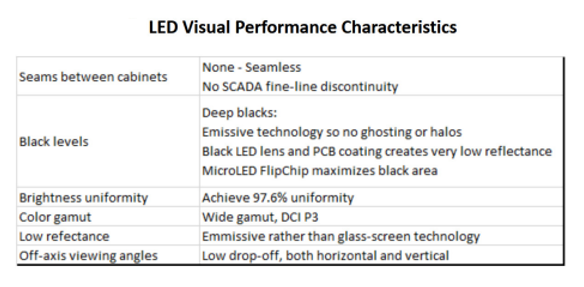
Visual Performance
The visual performance of control room video walls is of critical importance. As 24/7, mission-critical environments, important and often high-urgency decisions are being made based on visual information. Rear projection cubes today have a very limited number of viable use cases outside of control rooms, where their visual performance characteristics fit quite well. By contrast LED technology is used across a wide variety of applications, from high-ambient-light, distantly viewed corporate lobbies to light-controlled high-precision control rooms. As a result, it is important to select a LED display that is optimized for the control room environment, when done so, the visual performance characteristics will be an outstanding environment, and if done so, the visual performance characteristics can be outstanding.
Continuous Operation and Redundancy
Control rooms are often built around 24/7 continuous operational use. The video wall display must be designed to meet this requirement by being architected for continuous operations, high availability and redundancy. LED displays targeted at control rooms are designed for 24/7 continuous use and may offer additional redundancy features as well. They have no consumable parts like lamps, fans and filters that require repeated replacement.
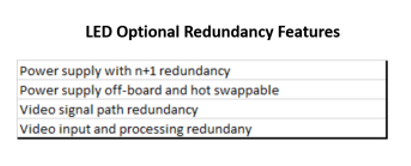
Modularity and Simplified Maintenance
For a control room display designed for long life and continuous mission-critical use, maintenance and reparability are key considerations. One of the greatest strengths of LED technology is its modularity and fast and simple repairability. From pixel to PCB module to power supply to video controller to interconnect cables, every component of a control room LED display is quickly reparable or replaceable on-site, from the front with no return-it-to-the-factory waiting and, often, without the need for specialized technicians.
The most uniquely beneficial portion of this modular architecture is the module; the magnetically attached PCB that contains the LED pixels on the front and the driver ICs on the back. It can be removed and replaced in minutes without disturbing the rest of the video wall and can actually be repaired at the pixel level either on the wall or when removed.

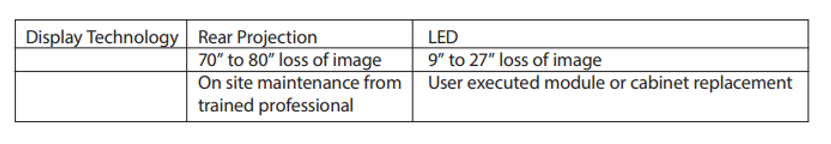
Less Intrusive Maintenance
Control rooms have 24/7 continuous operational use in critical operations. The video wall display must provide high operational availability. For that reason, potential failure and service is critical to uninterrupted control room operations. The smaller modules that make up LED video walls mean that a potential outage impacts only a small section of the overall display. Conversely, a display cube is much larger and therefore may provide for a significantly larger diagonal display area outage.
Warranty Coverage
A direct result of the inherent reliability of LED technology and its modular serviceability shows up in the outstanding warranties that manufacturers can offer on these products. Service costs are lower on LED technology and as a result, warranty coverage can be better. In order to deliver on a truly exceptional warranty, it is also necessary that the manufacturer has skilled technical personnel in the field near customers and that they have technical support, engineering, spares inventory and manufacturing and repair capability in the local geography.
Monitoring and Alerting
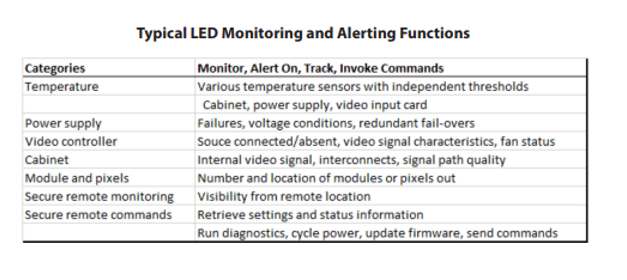
The control room operators have a job to do and should not be expected to be responsible for monitoring the health of the video wall. It is beneficial to have a video wall display that has internally instrumented components and can monitor and notify the appropriate maintenance technician in real time or at planned intervals. Modern LED control room displays incorporate monitoring capabilities across a wide range of key components and can expose trends and alert on a configurable set of conditions, whether the technician is local or across the country. Depending on the LED display in question, different levels of monitoring and alerting are available, but a reasonable list of monitoring capabilities to ask from the manufacturer include the following.
LED is an emissive display technology where power usage is tightly correlated to brightness and content. With LED technology, black means every pixel is off and full white, maximum brightness means every pixel (and subpixel) is on and at maximum luminance output. The first results in very low power usage and the second results in the maximum power spec for the display.
Content matters. In a typical SCADA or One-Line on a black background, regardless of maximum brightness level, power usage will be low because most of the pixels are off. This is in contrast to a projected image technology where the light source (and power consumption) is always maximized for a given brightness level regardless of content. All cubes include those using a laser light source, use pivoting micro-mirror DLP® technology. To achieve black the light is simply deflected away from the screen.
As a result, the relevant measure for operating power usage for a LED display must consider the brightness setting and the content being displayed. The following table compares power usage for a leading control room rear projection display and a control room LED display, when set to the same maximum full screen brightness level and when running SCADA content.
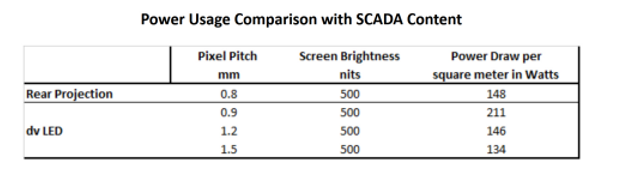
While LED displays often have the ability to deliver maximum brightness significantly above what rear projection can achieve, when run at lower brightness and with typical control room content, their actual power usage can be quite similar to that of rear projection.
Lifetime
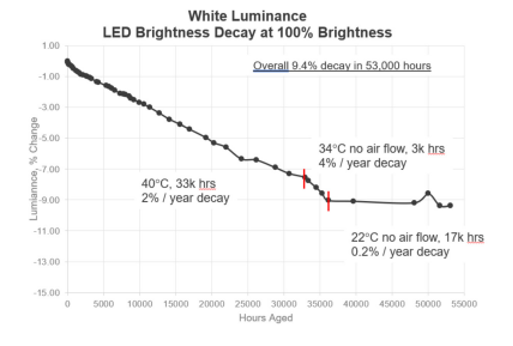
LED is an exceedingly stable and long-life technology. LED control room displays are typically specified to reach half brightness after 100,000 hours of maximum brightness, continuous operation. In reality, there is very little industry data on details or variations on the 100,000 hour specification. For this reason, Planar, in 2023, completed a 6+ year continuous life test of a 1.2mm pitch LED screen to add some real-life test data to the 100,000 hour number that the industry uses. Over the course of 53,000 hours of continuous, 100% brightness testing, the screen experienced a 9.4% decay in brightness. One pixel out of 25,920 failed during this time (0.004%). The pattern of brightness decay was linear rather than steeply dropping. Assuming the decay continued on a similar path, the display would have decayed to half brightness at 318,000 hours. This is only a single test, but based on the results, it seems very reasonable to expect that a high quality LED display might easily last 200,000 hours.
Conclusion
Control rooms represent an important and demanding application for video wall technology. While the incumbent technology of the past has been rear projection, increasing numbers of specifiers and customers are considering and using LED technology due to the inherent benefits that quality LED products deliver today. Looking forward, as the lion’s share of display industry investments continue to focus on LED technology, these solutions will become even better and more dominant in the future.

